Multiple sclerosis treatments
Outline:
- Introduction to Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Definition and overview
- Prevalence and impact
- Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
- Causes and risk factors
- Symptoms and diagnosis
- Conventional Treatments for Multiple Sclerosis
- Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs)
- Symptomatic treatments
- Emerging Therapies and Innovations
- Stem cell therapy
- Gene therapy
- Immunomodulatory treatments
- Alternative and Complementary Treatments
- Diet and nutrition
- Exercise and physical therapy
- Mind-body techniques
- Managing Symptoms and Enhancing Quality of Life
- Fatigue management
- Pain relief
- Cognitive rehabilitation
- Clinical Trials and Research Advancements
- Current trends and promising developments
- Patient participation and advocacy
- Holistic Approaches to MS Treatment
- Integrative medicine
- Lifestyle modifications
- Support groups and counseling
- Challenges and Considerations in MS Treatment
- Access to healthcare
- Side effects and risks
- Mental health and emotional well-being
- The Role of Healthcare Providers in MS Management
- Neurologists and specialists
- Allied health professionals
- Patient-centered care
- Personalized Medicine and Precision Treatments
- Tailored approaches to MS care
- Individualized treatment plans
- Long-Term Outlook and Prognosis
- Disease progression
- Strategies for long-term management
- Patient Empowerment and Self-Advocacy
- Education and awareness
- Empowering patients to take an active role in their treatment
- Supportive Care and Resources for Patients and Caregivers
- National MS Society and other organizations
- Financial assistance programs
- Caregiver support networks
- Conclusion
- Summary of key points
- Hope for the future of MS treatment
Multiple Sclerosis Treatments
Introduction to Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
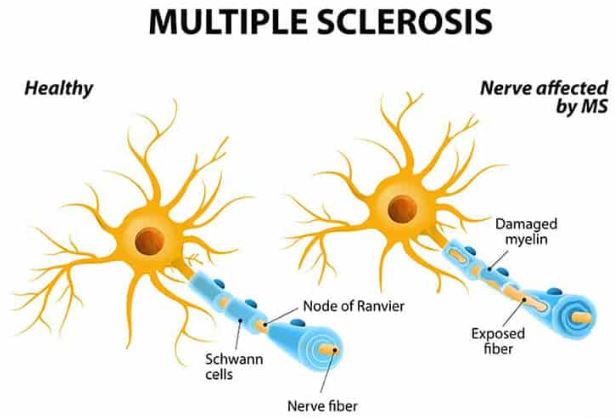
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). It is characterized by inflammation, demyelination, and scarring of the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers, leading to various neurological symptoms. MS is known to have a significant impact on the quality of life of those affected.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of MS is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Factors such as viral infections, vitamin D deficiency, and smoking have been implicated in increasing the risk of developing MS.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
MS can present with a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness or tingling, vision problems, and cognitive impairment. Diagnosis often involves a thorough medical history, neurological examination, and imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect lesions in the CNS.
Conventional Treatments for Multiple Sclerosis
Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs)
Disease-modifying therapies are designed to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, slow down disease progression, and delay disability accumulation in patients with MS. These treatments include interferons, glatiramer acetate, and newer medications such as monoclonal antibodies and oral therapies.
Symptomatic Treatments
Symptomatic treatments are aimed at managing specific symptoms of MS, such as spasticity, pain, bladder dysfunction, and depression. Medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Emerging Therapies and Innovations
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy involves the transplantation of stem cells to replace damaged cells and promote tissue repair in patients with MS. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this promising treatment approach.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to modify or replace faulty genes associated with MS to restore normal cellular function and immune regulation. Research in gene therapy holds potential for targeted and personalized treatments for MS in the future.
Immunomodulatory Treatments
Immunomodulatory treatments aim to regulate the immune system and prevent inflammatory attacks on the CNS in patients with MS. Novel immunotherapies targeting specific immune cells and pathways are being investigated for their potential role in MS management.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Diet and Nutrition
Dietary modifications, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, may help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms in patients with MS. Supplements such as vitamin D and probiotics are also commonly used to support immune function and gut health.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, balance, and mobility in patients with MS. Tailored exercise programs and rehabilitation strategies are important components of comprehensive MS care.
Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness-based stress reduction can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression in patients with MS. These practices promote relaxation, emotional well-being, and coping skills for managing the challenges of living with a chronic illness.
Managing Symptoms and Enhancing Quality of Life
Fatigue Management
Fatigue is a common and debilitating symptom of MS that can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life. Energy conservation strategies, lifestyle modifications, and pharmacological interventions may help manage fatigue and improve energy levels in patients with MS.
Pain Relief
Chronic pain, including neuropathic pain, musculoskeletal pain, and headaches, is prevalent in patients with MS and can be challenging to manage. Multimodal approaches combining medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies may provide effective pain relief and improve overall well-being.
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Cognitive impairment, including difficulties with memory, attention, and information processing, is a common manifestation of MS that can affect occupational and social functioning. Cognitive rehabilitation programs focus on improving cognitive skills, compensatory strategies, and adaptive functioning to maximize independence and quality of life.
Clinical Trials and Research Advancements
Current Trends and Promising Developments
Ongoing clinical trials and research studies are investigating novel treatments, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets for MS. Advances in genetics, immunology, and neuroimaging are shaping the future of MS research and offering new hope for improved outcomes and personalized therapies.
Patient Participation and Advocacy
Patient participation in clinical trials and research initiatives is critical for advancing our understanding of MS and developing new treatment options. Patient advocacy organizations play a vital role in raising awareness, funding research, and advocating for policies that support access to quality care for individuals living with MS.
Holistic Approaches to MS Treatment
Integrative Medicine
Integrative medicine combines conventional medical treatments with evidence-based complementary therapies to address the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of health and healing in patients with MS. Integrative approaches may include acupuncture, massage therapy, herbal medicine, and mind-body interventions to support overall well-being and symptom management.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction, smoking cessation, and maintaining a healthy weight can help optimize health outcomes and reduce disease activity in patients with MS. Adopting a balanced lifestyle with regular exercise, nutritious diet, and adequate sleep can support immune function, mood stability, and overall quality of life.
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups and counseling services provide emotional support, education, and practical resources for patients and caregivers coping with the challenges of MS. Peer support networks, online forums, and counseling sessions offer opportunities for sharing experiences, gaining insights, and building resilience in the face of adversity.
Challenges and Considerations in MS Treatment
Access to Healthcare
Access to specialized care, medications, and rehabilitation services may vary depending on geographic location, healthcare system, and insurance coverage. Addressing disparities in access to healthcare is essential for ensuring equitable and timely treatment for all individuals living with MS.
Side Effects and Risks
Many MS treatments, including disease-modifying therapies and symptomatic medications, can cause adverse effects such as injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms, and increased risk of infections. Healthcare providers monitor patients closely for side effects and adjust treatment regimens as needed to minimize risks and optimize safety.
Mental Health and Emotional Well-Being
Living with a chronic illness like MS can take a toll on mental health and emotional well-being, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Access to mental health services, peer support networks, and coping strategies is essential for addressing psychosocial challenges and promoting resilience in patients with MS.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in MS Management
Neurologists and Specialists
Neurologists with expertise in MS play a central role in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing the disease course in patients with MS. Multidisciplinary teams comprising neurologists, nurses, rehabilitation specialists, and other healthcare professionals collaborate to provide comprehensive and coordinated care for individuals living with MS.
Allied Health Professionals
Allied health professionals such as physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and social workers play integral roles in supporting functional independence, rehabilitation, and psychosocial well-being in patients with MS. Interdisciplinary care teams address the diverse needs and goals of individuals with MS across the lifespan.
Patient-Centered Care
Patient-centered care emphasizes collaboration, communication, and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers in MS management. Recognizing the unique preferences, values, and goals of each individual enables tailored treatment plans that align with their priorities and promote autonomy and empowerment in self-management.
Personalized Medicine and Precision Treatments
Tailored Approaches to MS Care
Personalized medicine aims to customize treatment strategies based on individual characteristics, including genetic makeup, disease subtype, and treatment response. Biomarkers and advanced imaging techniques enable clinicians to identify predictors of disease progression and tailor interventions to optimize outcomes and minimize risks in patients with MS.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Individualized treatment plans consider the unique needs, preferences, and priorities of each patient with MS, taking into account factors such as disease activity, symptom severity, comorbidities, and lifestyle factors. Shared decision-making and ongoing monitoring facilitate adjustments to treatment goals and strategies over time to maximize efficacy and safety.
Long-Term Outlook and Prognosis
Disease Progression
MS is a progressive disease characterized by relapses and remissions, with variable rates of disability accumulation and disease progression over time. Prognosis depends on factors such as age of onset, disease subtype, severity of symptoms, and response to treatment, with early intervention and comprehensive management strategies influencing long-term outcomes.
Strategies for Long-Term Management
Long-term management of MS focuses on preserving function, optimizing quality of life, and minimizing disease activity and progression through a combination of pharmacological, rehabilitative, and supportive interventions. Regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment regimens are essential for achieving and maintaining favorable outcomes in patients with MS.
Patient Empowerment and Self-Advocacy
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness initiatives empower patients with MS to become informed advocates for their health and well-being, fostering a sense of autonomy, self-efficacy, and resilience in managing their condition. Resources such as educational materials, online forums, and peer support networks facilitate knowledge-sharing and peer-to-peer support among individuals affected by MS.
Empowering Patients to Take an Active Role in Their Treatment
Empowering patients to take an active role in their treatment involves providing information, resources, and support to help them make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and navigate the healthcare system effectively. Encouraging self-management skills, self-monitoring strategies, and adherence to treatment plans enhances patient engagement and satisfaction with care in MS management.
Supportive Care and Resources for Patients and Caregivers
National MS Society and Other Organizations
The National MS Society and other patient advocacy organizations offer a wealth of resources, programs, and support services for individuals living with MS and their caregivers. These organizations provide information, advocacy, financial assistance, and community-based programs to improve quality of life and promote empowerment among those affected by MS.
Financial Assistance Programs
Financial assistance programs help alleviate the financial burden of MS care by providing access to medication assistance, insurance coverage, disability benefits, and financial aid for medical expenses and supportive services. Patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies and nonprofit organizations help ensure affordability and access to essential treatments for individuals with MS.
Caregiver Support Networks
Caregiver support networks provide emotional support, education, and practical resources for family members, friends, and caregivers of individuals with MS. Respite care, counseling services, and caregiver training programs offer opportunities for self-care, stress management, and coping skills development to enhance caregiver well-being and resilience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multiple sclerosis is a complex and challenging condition that requires a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to treatment and management. With advances in research, innovation, and patient-centered care, there is hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with MS. By promoting education, empowerment, and support for patients and caregivers, we can enhance resilience, autonomy, and well-being in the MS community.
Unique FAQs
1. Can multiple sclerosis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for multiple sclerosis. However, various treatments and management strategies can help control symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life for individuals living with MS.
2. Are there alternative treatments for multiple sclerosis?
Yes, many individuals with MS explore alternative and complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body techniques to complement conventional treatments. It’s essential to discuss these options with healthcare providers and ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific needs.
3. What are the common side effects of MS medications?
Common side effects of MS medications may include injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms, gastrointestinal disturbances, and increased risk of infections. It’s essential to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider and report any concerns promptly.
4. How can I manage fatigue associated with multiple sclerosis?
Fatigue management strategies may include pacing activities, prioritizing tasks, conserving energy, maintaining a balanced lifestyle, and incorporating relaxation techniques. Working with healthcare providers to address underlying factors contributing to fatigue can also be beneficial.
5. Where can I find support and resources for living with multiple sclerosis?
There are many resources available for individuals living with MS and their caregivers, including national organizations such as the National MS Society, online support groups, local community services, and healthcare professionals specializing in MS care. Seeking out these resources can provide valuable information, support, and connection with others who understand your experiences.